
Do I have to charge VAT as a Sole Trader?
As a Sole Trader, you can benefit from basic VAT exemption.
VAT exemption means you don't have to charge VAT on your invoices (your invoices must not be entitled "VAT invoice" or "Tax Invoice"). In principle, you don't have to file a VAT return.
On the other hand, you won't be able to "recover" the VAT on your business expenses.
To qualify for the basic VAT exemption, your sales (earnings) must not exceed £85,000 over the last 12 months.
More information here: Register for VAT (GOV.UK)
Leaving the VAT exemption scheme has the following effects:
You must register with HMRC within 30 days of the end of the month in which you exceeded the £85,000 limit.
Transactions carried out from the 1st day of the second month after the limit was exceeded are subject to VAT.
In principle, you can deduct VAT on your business expenses incurred on or after this date.
Example: I receive £2,500 on May 14, 2024. My total sales for the last 12 months (May 15, 2023 - May 14, 2024) exceed the limit of £85,000. I must therefore register by June 30, 2024. I will be subject to VAT from July 1, 2024.

What if I think I'll temporarily exceed the limit?
You can request an "exception" from VAT exemption if you consider that your sales temporarily exceed the £85,000 limit.
In this case, you need to write to HMRC, enclosing evidence to show that your turnover is expected to be less than £83,000 over the next 12 months (the threshold for a possible return to VAT-free status).
HMRC will consider your request and write to you to confirm whether you qualify for this exception. If not, HMRC will register you for VAT.
I'm under the limit, can I voluntarily opt to pay VAT?
Yes, it is entirely possible to request that you be registered for VAT, even if you are under the £85,000 limit. This request can be made:
Online, via your "Government Gateway" account
By post, using the "VAT1" form
By an agent (e.g. an accountant)
The option takes effect on the day chosen by the taxpayer.
So, to opt or not to opt?
Whether or not to opt for VAT payment will depend on several factors:
Pros:
Invoicing VAT gives me the right to reclaim VAT on my business expenses.
Invoicing VAT has a neutral impact on my business relations with other professionals who can deduct VAT.
Charging VAT can give your customers the impression that you're already over the tax-free threshold, reinforcing your image as a professional.
Some customers even require their supplier to invoice them for VAT.
I don't have to worry about exceeding the £85,000 threshold and avoid penalties for late reporting
Cons:
Charging VAT will require me to file regular VAT returns
Charging VAT may increase the cost of my services if the customer cannot deduct the VAT charged (e.g.: a private individual, an association, a school, a healthcare institution, etc.).
What do I have to do on Malt if I exceed the VAT threshold or opt for VAT?
You need to verify that you are registered as a Sole Trader or Ltd as your legal form..
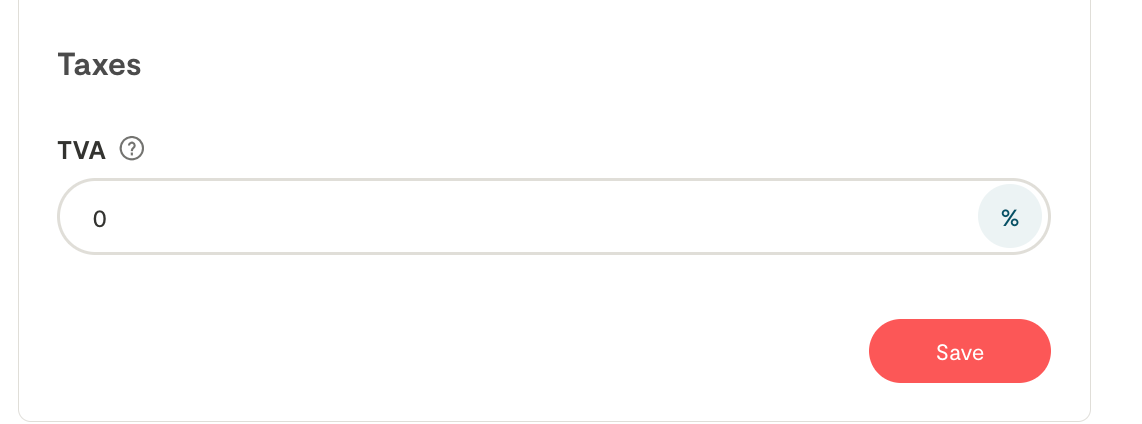
You must enter 20% in the "Taxes" tab of your profile.
You can then modify your projects:
Project in progress (invoice not issued):
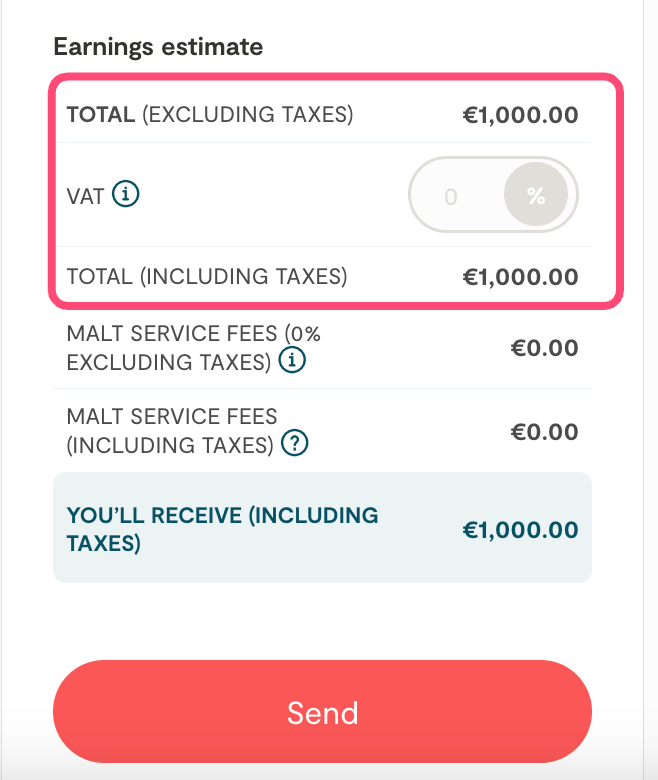
In the case of a task-based project, you can then modify the quote directly from the assignment URL and manually adjust the VAT to a rate of 20%.
For time-based projects, please contact support@malt.uk so that we can update the job for invoices not yet issued.
Project completed (invoice issued):
You will need to contact your customer to obtain their written agreement to re-open the invoice(s). Proof of the customer's acceptance (email or screenshot) and the invoice number to be modified must be sent to support@malt.uk. We will then issue a credit note for the amount already paid, and draw up a new invoice including VAT.
I run my business as an Ltd or Partnership. Do I have VAT exemption?
A company or partnership can also benefit from basic VAT exemption under the same threshold conditions as a Sole Trader.

International VAT management
Invoicing a foreign customer
In a B2B relationship, you don't charge VAT. Ideally, your invoice should mention your foreign customer's intracommunity VAT number (or equivalent) and indicate "reverse charge for services - customer to account for the VAT".
In a B2C relationship, you don't charge VAT for intangible services (e.g. consulting).
You receive an invoice from a foreign-based supplier (including the costs of a foreign Malt entity).
In principle, the foreign-based service provider should not charge you VAT if you are a business (a VAT taxable person).
However, if you are registered for VAT in the UK, then you will need to reverse charge VAT on services supplied by an overseas supplier. This means that you will have to pay UK VAT at the rate of 20% on this invoice and report this amount on your VAT return.
In principle, this reverse-charge VAT can be deducted on your VAT return (and will therefore have a neutral effect on your situation).
Please note: If you benefit from VAT exemption, you must apply to HMRC for a VAT number if you are acquiring goods or services from a supplier established in the EU.
For more information on international VAT, click here.
